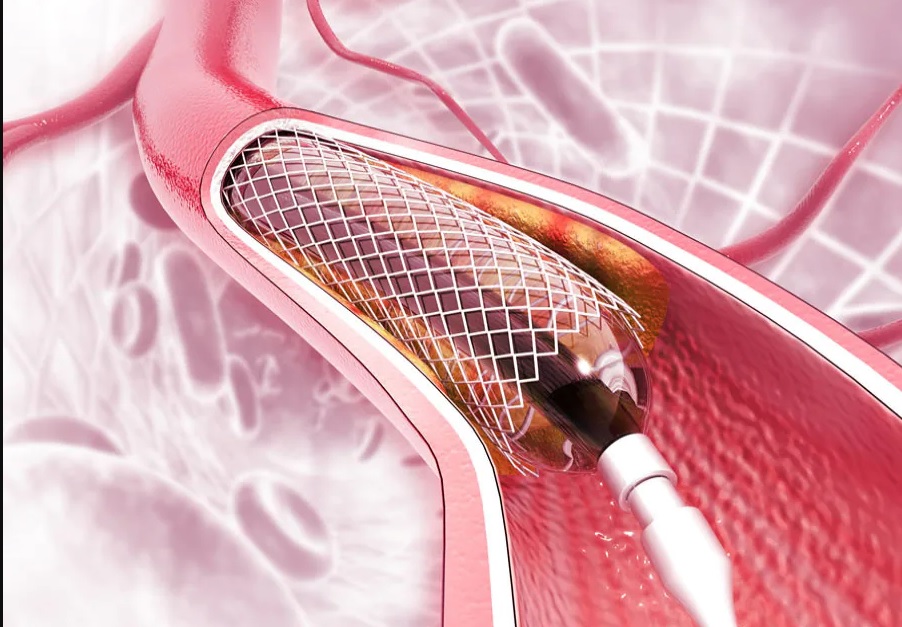
A coronary angioplasty is a procedure used to widen blocked or narrowed coronary arteries (the main blood vessels supplying the heart)
The term "angioplasty" means using a balloon to stretch open a narrowed or blocked artery However, most modern angioplasty procedures also involve inserting a short wire-mesh tube, called a stent, into the artery during the procedure The stent is left in place permanently to allow blood to flow more freely
Coronary angioplasty is sometimes known as percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) The combination of coronary angioplasty with stenting is usually referred to as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
A coronary angioplasty is performed which means you&#ll be awake while the procedure is carried outA thin flexible tube called a catheter will be inserted into one of your arteries through an incision in your groin, wrist or armWhen the catheter is in place, a thin wire is guided down the length of the affected coronary artery, delivering a small balloon to the affected section of artery This is then inflated to widen the artery, squashing fatty deposits against the artery wall so blood can flow through it more freely when the deflated balloon is removed
If a stent is being used, this will be around the balloon before it&#s inserted The stent will expand when the balloon is inflated and remains in place when the balloon is deflated and removed
A coronary angioplasty usually takes between minutes and hours If you&#re being treated for angina, you&#ll normally be able to go home later the same day or the day after you have the procedure You&#ll need to avoid heavy lifting, strenuous activities and driving for at least a week
If you&#ve been admitted to hospital following a heart attack, you may need to stay in hospital for several days after the angioplasty procedure before going home